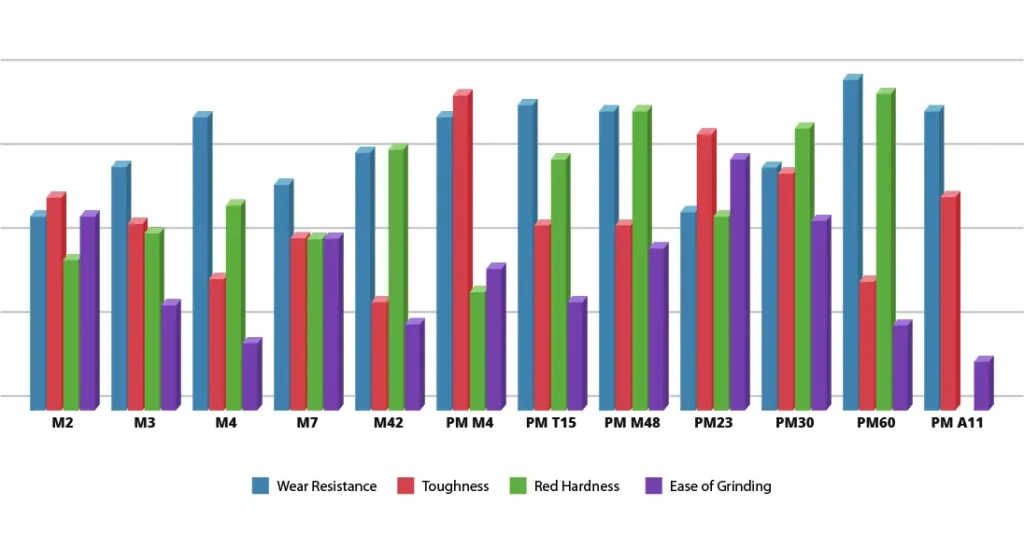
M2 High speed tool steel is made from tungsten and molybdenum. M2 is well-balanced in toughness, wear resistance, and red hardness properties. Due to its superior properties and advantageous prices, M2 has largely replaced T1 in most applications. M2 is medium-alloyed and is a good all-round performer with good machinability, so it outperforms high alloyed cold work steels. Related Specifications : DIN1.3343
Applications of M2 High Speed Tool Steel
M2 is a widely-utilized cutting tool due to its balanced properties. Common uses are for tools that require moderate hot hardness, like twist drills, reamers, broaches, milling cutters, taps and metal saws. It is also suitable for cold work applications which include tools for punching, forming and pressing. If a higher level of red-hardness is desired then M42 high speed steel should be considered. To see all the applications for M2 check out our tool steel application chart which includes items such as broaches, knives, drills, pins, reamers, taps and thread roll dies.
Chemical Composition of M2 High Speed Steel
| Carbon | Chromium | Tungsten | Molybdenum | Vanadium | Cobalt | Annealed | Tempered |
| C | Cr | W | Mo | V | Co | Hb | HrC |
| 0.85 | 4.15 | 6.15 | 5.1 | 1.95 | – | 255 | 64 |
M2 High Speed Steel Heat Treating
| Annealing | Preheat | Austenttizing | Quench | Tempering |
| Temp °F | Temp °F | Temp °F | Medium | Temp °F |
| 1550/1600 | 1500/1550 | 2175/2225 | Salt/Oil/Atm | 1025/1050 |
Thermal Treatments of M2 High Speed Steel
Preheating
To minimize distortion and stresses in large or complex tools use a double preheat. Heat at a rate not exceeding 400°F per hour (222°C per hour) to 1100°F (593°C) equalize, then heat to 1450-1550°F (788-843°C). For normal tools, use only the second temperature range as a single preheating treatment
Annealing
After hot working and before re-hardening, anealing should be performed. Heat at a temperature not exceeding 400°F per hour (222°C per hour) to 1525-1550°F (829-843°C) and hold at that temperature for at least 2 hours per inch (25.4 mm) in thickness. Cool slowly with the furnace at not more than 50°F per hour (28°C per hour) to 1000°F (538°C) until the room reaches ambient temperature.
Quenching
The desired properties can be achieved with pressurized gas, warm oil, or salt. For pressurized gas, a rapid quench rate to below 1000°F (538°C) is crucial. When quench oil until black, about 900°F (482°C), cool it to 150-125°F (66-51°C) in still air. At 1000-1100°F (538-593°C), equalize it, then cool it to 150-125°F (66-51°C) in still air.
Tempering
Hold at temperature for 2 hours, then air cool to ambient temperature. Temper immediately after quenching. Typical tempering temperature is 1025-1050°F (552-566°C). For large cross sections, and especially for blanks from which tools will be cut by wire EDM, triple tempering is highly recommended.
Austenizing (High Heat)
- Heat rapidly from the preheat.
- For Cutting Tools: Furnace: 2200-2250°F (1204-1232°C); Salt: 2175-2225°F (1191-1218°C)
- To maximize toughness, use the lowest temperature. To maximize hot hardness, use the highest temperature.
- For punches, dies, and tools that require maximum toughness without hot hardness:
- Furnace: 2075-2175°F (1175-1191°C); Salt: 2050-2150°F (1121-1177°C)
IBC (Tianjin) Industrial Co., Ltd is a large special steel manufacuter & supplier & exporter. We are metal experts and have been providing quality customer service and products. Our hot rolled and cold rolled steel is available in a wide range of shapes including: bars, tubes, sheets and plates. We can cut metal to your exact specifications. For more information, please contact with us today.

Contact with us today!



