IBC (Tianjin) Industrial Co., Ltd produce & export high speed tool steel to all over the world for decades years. High Speed Tool Steels and their requirements are defined by The American Society for Testing and Materials in Specification A600-79. Including many kinds of products, such as T1. T4, T5 high speed tool steel, and M2, M35, and M42 high speed tool steel and so on.


High-speed tool steels are called so due to their capacity to machine materials at high speeds. Said alloys are composed of a blend of carbon, chromium, vanadium, molybdenum or tungsten. Or some combination of these elements. And may also incorporate sizeable amounts of cobalt. To obtain an efficient industrial cutting performance, the elements must be carefully balanced. So as to provide robust hardening capabilities, prolonged wear resistance. And superior resistance to thermal softening all with satisfactory toughness.
Our main products:
- Product: high speed steel
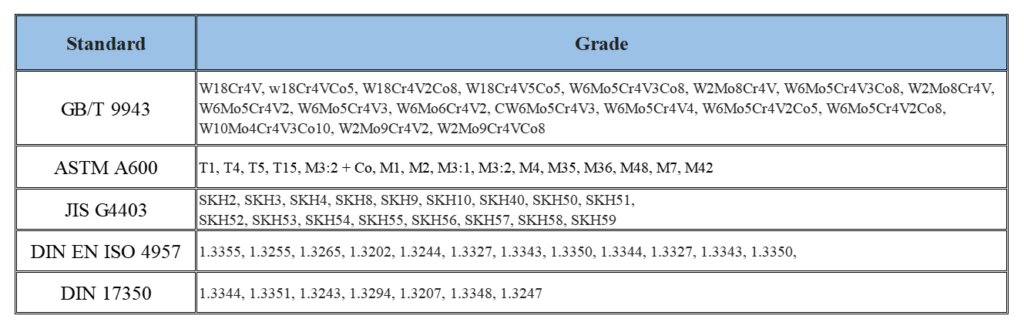
- Standards: ASTM A600, JIS G4403, DIN 17350
- Application: milling cutters, drills, taps, planar and joint cutters, saw blades etc.
- Grade: ① T1, T4, T5, T15; ② M1, M2; ③ SKH2, SKH3, SKH4, SKH9, SKH10; ④ DIN 1.3355, DIN 1.3255, DIN 1.3343
Surface Treatments
For non-ferrous or ferrous metals, high speed steel tools are often finished with bright or black oxide. Nitriding diffuses nitrogen into the surface of the steel during heat treatment, resulting in a case-hardened surface with higher wear resistance at the expense of notch hardness. Other coatings and treatments are also possible.
Titanium nitride (TiN) via physical vapor deposition is Another common treatment. Which enhances edge retention significantly. This, combined with a lower coefficient of friction, means an extended lifespan and improved machining, though TiN-coated tools react adversely with titanium or nickel alloys.
Factors in Selecting High Speed Tool Steels
No one composition of high-speed tool steel can meet all cutting tool requirements. Tungsten steel T I and M l, M2, and M7 are general-purpose molybdenum steels. They more commonly used than other high-speed tool steels. They have the highest toughness and good cutting ability. But they possess the lowest hot hardness and wear resistance of all the high-speed tool steels. The addition of vanadium offers the advantage of greater wear resistance and hot hardness. And steels with intermediate vanadium contents suited for fine and roughing cuts on both hard and soft materials. The 5% V steel (TI5) especially suited for cutting hard metals and alloys or high-strength steels. And particularly suitable for the machining of aluminum, stainless steels, austenitic alloys, and refractory metals. Wrought high-vanadium high-speed tool steels are more difficult to grind than their P/M product counterparts. The addition of cobalt in various amounts allows still higher hot hardness. The degree of hot hardness being proportional to the cobalt content. Although cobalt steels more brittle than the noncobalt types. They give better performance on hard, scaly materials that machined with deep cuts at high speeds.
In spite of the inroads made by competitive cutting tool materials like cast cobalt alloys, cemented carbides, ceramics, and cermets, high-speed tool steels continue to be important in industrial commerce for 70 to 80 years. In the market for cutting tool materials, high speed tool steels are renowned for their superior toughness.
Application of High Speed Tool Steel
Tool Steel High Speed is a cutting tool material used in drilling, milling, turning, threading, boring, broaching, gear cutting and many other machining operations. High Speed Steel used for form tools, slitter knives, guillotine knives, parting tools and many other types of cutting tools. It cutting tools used in all phases of production. And widely used in both machine tools and in portable machine tools.
Broadly, high speed steel excels in hardness and abrasion resistance, with different grades trading for toughness, hot hardness or reduced brittleness. As a result, these alloys see the most use in industrial cutting tools. — tool bits, milling cutters, saw blades, drills, taps, broaches and more.
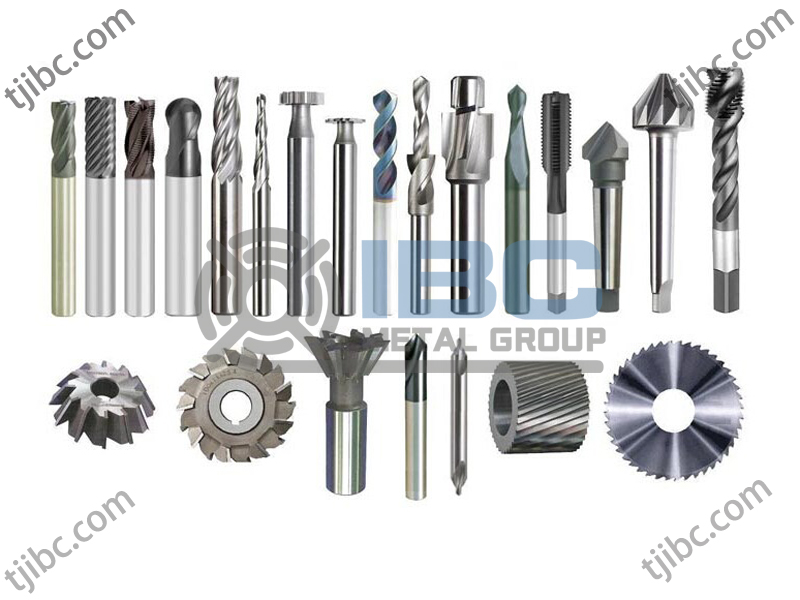

Tools made of high speed steel frequently keep a sharp edge for longer than other carbon steels. And the variety of grades and surface treatments available provide options for specialized applications. These products see use anywhere from woodworking to machining high-grade alloys.
Though not traditionally considered to be cutting tools, punches, dies. And other components in progressive stamping can also be made from high speed steel. Additionally, the properties of high speed steels, particularly hardness and wear resistance. It is desirable for hand tools such as chisels, files, blades for hand planes and kitchen and pocket knives.
Conclusion
For decades, IBC Metal Group has provided quality high speed tool steel to many clients. All for all of their machining and fabrication needs. Our standards for both our products and service keep us moving forward to satisfy customers. And build lasting relationships with them. For more information or you need this product in your projects, please contact with us.

Contact with us!



